How to assess the quality of any backlink (paid, earned, sponsored or otherwise)
In my years of experience, there are only 2 types of backlinks.
- Backlinks that add value, and;
- Backlinks that offer no value.
And let’s be honest. You’re here and wanting to get more backlinks because you believe they play a role in ranking webpages on Google SERPs.
And you wouldn’t be wrong.
Everything in SEO works until it doesn’t and this rings true for all types of links – comment spam, guest posts, directory submissions, niche edits, resource page links, skyscraper method, broken link reclamation etc. This is because every hyperlink can serve a purpose but once the purpose is served, acquiring more of it is a waste of time, money and resources.
But there’s only one person you should trust when it comes to assessing the quality of a backlink.
It’s not me.
It’s not some SEO influencer.
The only person you should trust is yourself.
And to do this right, follow my 22 point checklist on how to qualify any type of backlink – earned, bought, or otherwise.
📌 Why you can trust me: Many guides on backlink audits are written by backlink vendors or SEO tools. I, on the other hand, don’t offer link building services. Instead, I’m sharing everything I’ve learnt since my agency days and my experience as an in-house enterprise SEO.
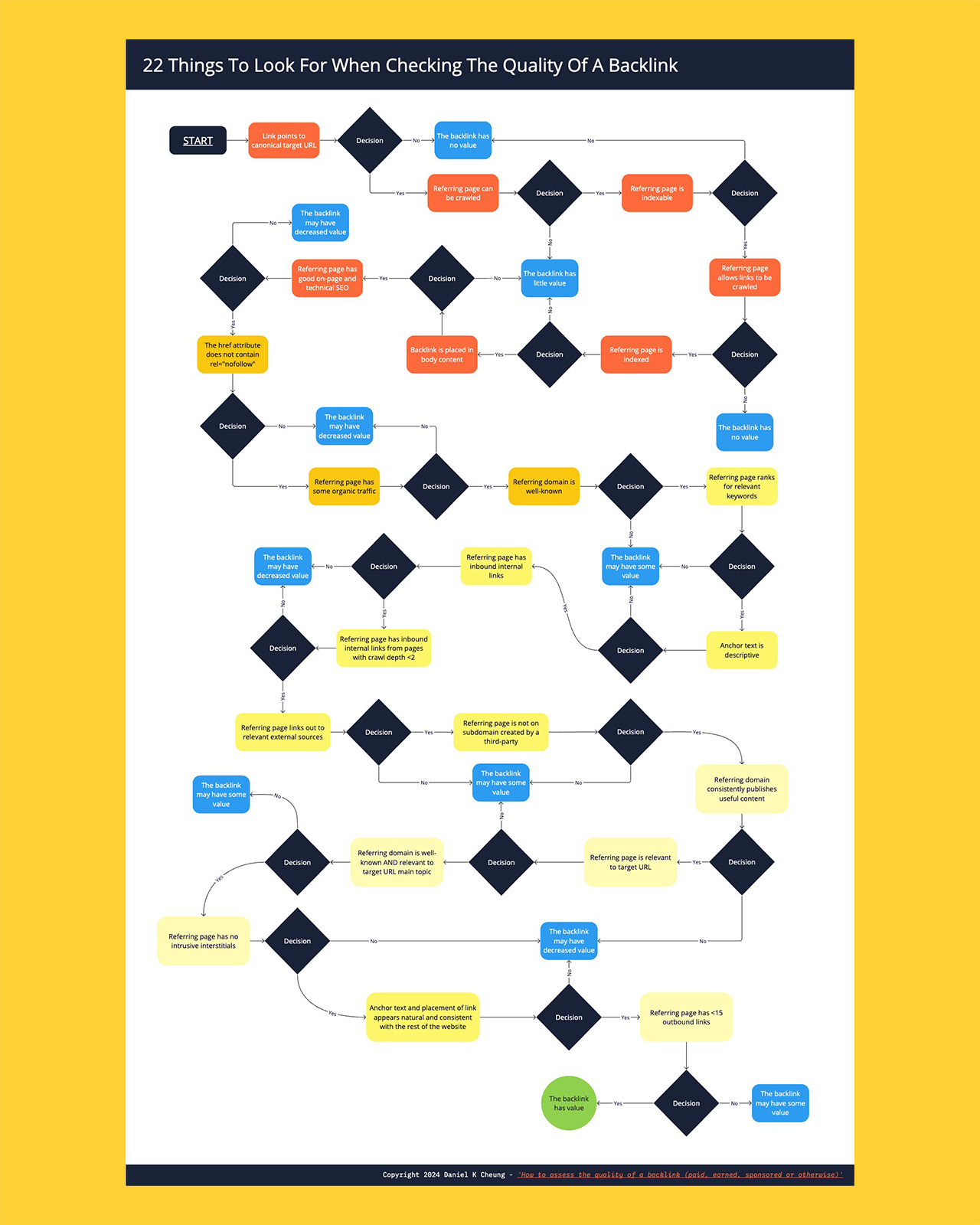
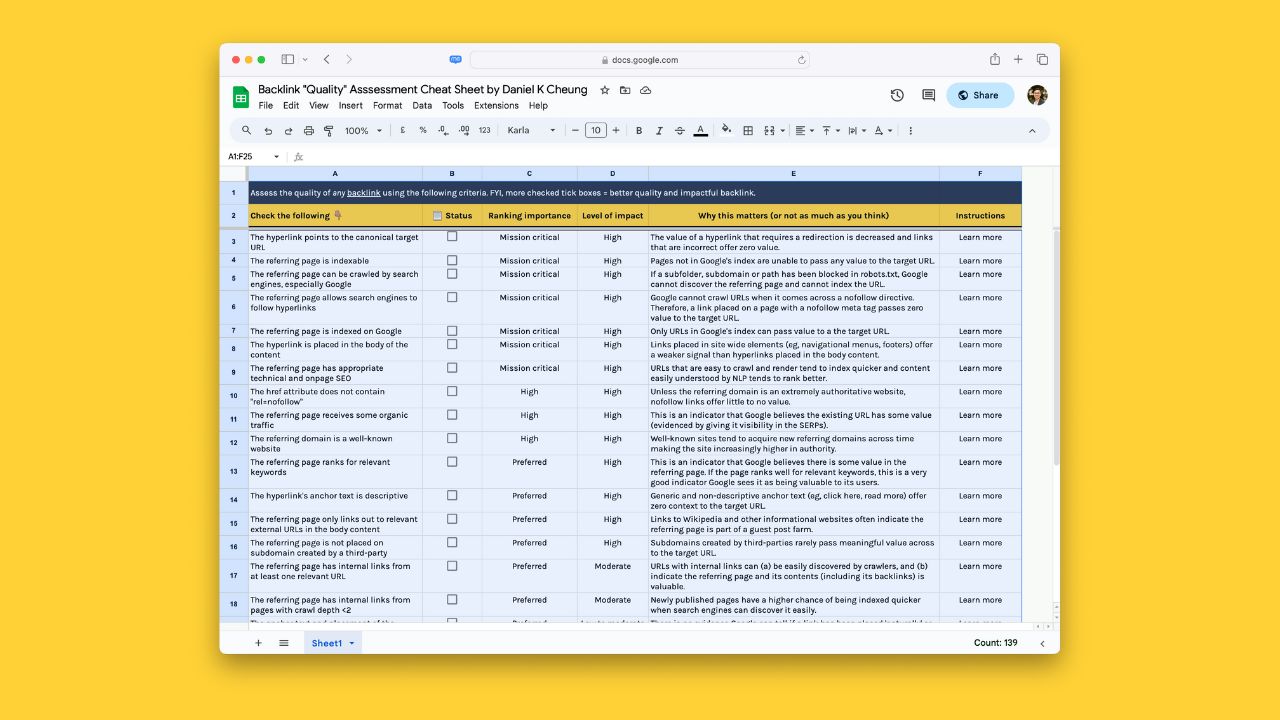
22 things to look for when checking the quality of a backlink
There are 22 criteria by which to evaluate a backlink.
Let’s get started.
The hyperlink points to the canonical target URL
Level of importance: Mission critical – the backlink must take people and bots directly to the target URL.
Why this matters: The value of a hyperlink that requires a 301 or 302 redirection is decreased and links that are incorrect (ie, pointing to an incorrect URL) offer zero value to you.
Level of impact: Extremely high
How to check
- Right click on the hyperlink and copy the URL address
- Go to https://httpstatus.io/ and paste in the URL
- Untick ‘Canonical domain check’ before clicking ‘Check status’
- ✅ Pass: A single 200 status code is shown
- ⚠️ Fail: One or more 3XX status codes are shown or a 4XX or 5XX status code
What to do when the backlink does not point to the canonical target URL: Ask your link vendor to copy and paste the correct target URL.
The referring page can be crawled by search engines, especially Google
Level of importance: Mission critical – Google will not index URLs it cannot crawl.
Why this matters: On the surface the backlink may pass most superficial checks. But if the subfolder, subdomain or path has been blocked in the referring domain’s robots.txt file the backlink serves absolutely no purpose and offers zero value to you.
Level of impact: Extremely high
How to check
- Load the root domain or subdomain in any web browser
- Append robots.txt to the end of the URL and press enter/return to load the file
- Scan for any lines in the file that starts with “disallow”
- ✅ Pass: The referring page’s path is not block by robots.txt
- ⚠️ Fail: The referring page’s path is blocked by robots.txt
What to do when the page cannot be crawled by search engines: Ask your link vendor for a refund or a replacement link.
The referring page is indexable
Level of importance: Mission critical – the backlink must be placed on a page that is indexed on Google. And for this to happen, the referring page must be indexable.
Why this matters: Pages not in Google’s index are unable to pass any value to the target URL.
Level of impact: Extremely high
How to check
- Install SEO Pro Extension on Chrome
- Once installed, load the referring page in your Chrome browser
- Open SEO Pro Extension and inspect the Meta Robots line
- ✅ Pass: The field says “index”
- ⚠️ Fail: The field says “noindex”
What to do when the page cannot be indexed: Ask your link vendor why they have marked the page as noindex. If you paid for the placement, demand a refund or get it fixed.
The referring page allows search engines to follow hyperlinks
Level of importance: Mission critical – even if the referring page is indexed, if Google comes across a nofollow directive, it will not crawl the hyperlink that is pointing to the target URL.
Why this matters: Google cannot crawl URLs when it comes across a nofollow directive. Therefore, a link placed on a page with a nofollow meta tag passes zero value to the target URL.
Level of impact: Extremely high
How to check
- Install SEO Pro Extension on Chrome
- Once installed, load the referring page that links to your target URL
- Open SEO Pro Extension and inspect the Meta Robots line
- ✅ Pass: The field says “index, follow”
- ⚠️ Fail: The field says “nofollow”.
What to do when the page contains a nofollow directive: Ask your link vendor why they have marked the page as nofollow. If you paid for the placement, demand a refund or have the nofollow directive overturned.
The referring page is indexed on Google
Level of importance: Mission critical – the backlink must be placed on a page that is indexed on Google.
Why this matters: Pages not in Google’s index are unable to pass any value to the target URL. Just because the page is marked as indexable does not mean it is actually indexed.
Level of impact: Extremely high
How to check
It is highly unlikely a link vendor can give you proof from Google Search Console on the indexing status of a referring page. Therefore, the next best option is to use an approximation.
While not perfect, the site: operator function can provide a strong indication of whether or not the referring page is indexed or not.
In any web browser, type into Google search bar:
site:{full URL of the referring page}
eg, site:https://www.danielkcheung.com/semantic-seo-beginners-guide/- ✅ Pass: You see the referring page shown in the SERP (this indicates Google is aware of the URL and there is a high likelihood the URL is indexed)
- ⚠️ Fail: You cannot see the referring page shown (this indicates Google is unaware of the URL)
What to do when the referring page is not indexed: If the referring page was published recently, it is plausible it may not be indexed. First, do your due diligence to make sure the URL is indexable. If it can be indexed, give it some time but remember to check back in a week’s time. If, however, the backlink was a niche edit, ask your link vendor why they placed a link on a non-indexed page and demand they replace the link on a indexed page or refund you.
The hyperlink is placed in the body of the content
Level of importance: Mission critical – the backlink must be placed in the body content of the referring page.
Why this matters: Links placed in site wide elements (eg, navigational menus, footers) offer a weaker signal than hyperlinks placed in the body content. More importantly, when done properly, hyperlinks in the body appear more natural and less spammy.
Level of impact: High
How to check: Load the referring page in any web browser and manually look for the backlink.
- ✅ Pass: The hyperlink is found in the main body content of the referring page.
- ⚠️ Fail: The hyperlink is placed in the footer or side bar.
The referring page has appropriate technical and on-page SEO
Level of importance: High
Why this matters: URLs that are easy to crawl and render tend to index quicker and content easily understood by NLP tends to rank better.
Level of impact: High
How to check
- ✅ Pass: The referring page has:
- Keyword optimised page title
- Keyword optimised h1
- Correct use of h1-h6 tags
- Written text is web-appropriate (eg, short and simple sentences and paragraphs)
- Main content does not require JavaScript to the rendered (ie, raw HTML = rendered HTML)
- One or more internal URLs link to the referring page using descriptive anchor text
- ⚠️ Fail: The referring page has:
- No h1-h6 structure
- Long walls of text with little to no formatting
- No implementation of pre-rendering to ensure raw HTML = rendered HTML
- No incoming internal links
- Inbound internal links with generic anchor text (eg, click here, learn more, read more)
The href attribute does not contain rel=”nofollow”
Level of importance: High – however, in certain instances, a nofollow backlink from a very well-known website (e.g., Wikipedia) is better than no backlink at all.
Why this matters: Unless the referring domain is an extremely authoritative website and the referring page can provide the target URL with substantial referral traffic, nofollow links offer little to no value.
Level of impact: High
How to check
- Load the referring page in any web browser (eg, Chrome)
- Find the backlink, right click on the link, and click ‘Inspect’
- See if there is rel=”nofollow” within the <a> tag
- ✅ Pass: The HTML does not contain rel=”nofollow”
- ⚠️ Fail: The HTML contains rel=”nofollow”
The referring page for the link insertion receives some organic traffic
Level of importance: High
Why this matters: This is an indicator that Google believes there is some value in the referring page. When getting a link inserted into an existing URL, you’ll want a page that has some keyword rankings that bring in search engine traffic.
Level of impact: High
How to check
Put the referring page into any third-party SEO tool such as Semrush, Similar Web, Ahrefs, or Moz.
- ✅ Pass: The referring page receives >10 organic traffic
- ⚠️ Fail: The referring page receives no organic traffic
The referring domain is a well-known website (to you or the topic’s target audience)
Level of importance: High
Why this matters: Well-known sites tend to acquire new referring domains across time making the site increasingly higher in authority.
Level of impact: High
How to check
Every industry and niche has its list of reputable websites and publishers. If you do not know what these are use SaaS solutions such as SparkToro or Bombora for B2B user intent insights.
Alternatively, put your competitor URLs into SaaS tools such as Ahrefs to see what referring domains they have from high DR and high traffic websites.
- ✅ Pass: The referring domain is well-known to you or the target audience
- ⚠️ Fail: The referring domain is not well-known
The referring page ranks for relevant keywords
Level of importance: Preferred
Why this matters: This is an indicator that Google believes there is some value in the referring page. If the page ranks well for relevant keywords, this is a very good indicator Google sees it as being valuable to its users.
Level of impact: High
How to check
Put the referring page into your SEO tool of choice (eg, Ahrefs, Semrush, Moz, SE Ranking) to see what keywords it ranks for.
- ✅ Pass: The referring page ranks for multiple relevant keywords
- ⚠️ Fail: The referring page ranks for irrelevant keywords or does not rank for any keywords at all
The hyperlink’s anchor text is descriptive
Level of importance: Preferred
Why this matters: Generic and non-descriptive anchor text (eg, click here, read more) offer zero context to the target URL. An exact match, partial match, or phrase match anchor text makes it easier for search engines to understand the context and relationship of the target URL to the referring page.
Level of impact: High
How to check
- Read the article ‘What is Anchor Text?’ by Jonas Sickler, published on Terakeet
- Open the referring page and find the hyperlink pointing to the target URL
- Identify what type of anchor text is being used
- ✅ Pass: Anchor text is exact match, partial match or phrase match
- ⚠️ Fail: Anchor text is blank, naked URL, or generic
The referring page has internal links from at least one relevant URL
Level of importance: Preferred
Why this matters: URLs with internal links can (a) be easily discovered by crawlers, and (b) indicate the referring page and its contents (including its backlinks) is valuable.
Level of impact: Moderate
How to check
- Use a web crawler such as Screaming Frog SEO Spider Website Crawler
- Crawl the entire website or an appropriate sample of pages (eg, subfolder, subdomain)
- Find the referring page in the ‘Internal’ tab > click on the ‘Inlinks’ tab
- ✅ Pass: One or more referring pages are listed in the ‘Inlinks’ tab
- ⚠️ Fail: No referring pages are listed in the ‘Inlinks’ tab (even after crawling the entire website) or the referring page cannot be found in the ‘Internal’ tab.
The referring page has internal links from pages with crawl depth <2
Level of importance: Preferred
Why this matters: Newly published pages have a higher chance of being indexed quicker when search engines can discover it easily.
Level of impact: Moderate
How to check
- Use a web crawler such as Screaming Frog SEO Spider Website Crawler
- Crawl the entire website or an appropriate sample of pages (eg, subfolder, subdomain)
- Find the referring page in the ‘Internal’ tab and navigate to the ‘Crawl Depth’ column
- ✅ Pass: The referring page’s crawl depth from the homepage is less than 2
- ⚠️ Fail: The referring page’s crawl depth from the homepage is greater than 2
The referring page only links out to relevant external URLs in the body content
Level of importance: Preferred
Why this matters: Links to Wikipedia and other informational websites often indicate the referring page is part of a guest post farm.
Level of impact: High
How to check
- Install SEO Pro Extension on Chrome
- Once installed, load the referring page that links to your target URL
- Open SEO Pro Extension and go to the ‘Links’ tab and look at the ‘External links’ drop-down:
- ✅ Pass: External links are relevant and make sense
- ⚠️ Fail: External links go to needlessly informational websites such as Wikipedia, Forbes, Healthline
The referring page is not placed on subdomain created by a third-party
Level of importance: Preferred
Why this matters: Subdomains created by third-parties rarely pass meaningful value across to the target URL.
Level of impact: High
How to check
- ✅ Pass: The referring page sits on a section of the website maintained by root domain administrators
- ⚠️ Fail: The referring page sits on a subdomain created by a third-party not maintained by the root domain administrators
The referring domain consistently publishes useful content
Level of importance: Nice to have
Why this matters: This is a strong indicator the website is a reputable one, especially if its pages consistently gains organic traffic from a growing set of organic keywords.
Level of impact: Moderate
How to check
Find the blog section of the referring domain:
- ✅ Pass: The referring domain consistently publishes useful content
- ⚠️ Fail: The referring domain does not consistently publish useful content
The hyperlink is placed on a referring page that is relevant to the target URL
Level of importance: Nice to have
Why this doesn’t matter: Relevance of a referring page is overrated and in real world situations, the context of a paragraph that links to you may be topically different to that of the body content (eg, a quote).
Level of impact: Low to moderate
How to check
Load the referring page in a web browser and scan the content of the page:
- ✅ Pass: The topic of the referring page is directly relevant to the target URL
- ⚠️ Fail: The topic of the referring page is not relevant to the target URL
The referring domain is a well-known and relevant to main topic of the target URL
Level of importance: Nice to have
Why this matters: Backlinks from a well-known and relevant referring domain can increase the likelihood of referral traffic.
Level of impact: High
How to check
Every industry and niche has its list of reputable websites and publishers. If you do not know what these are use SaaS solutions such as SparkToro or Bombora for B2B user intent insights.
- ✅ Pass: The referring domain is well-known and relevant to the main topic of the target URL
- ⚠️ Fail: The referring domain is not well-known or is not relevant to the main topic of the target URL
The referring page does not have intrusive interstitials
Level of importance: Nice to have
Why this doesn’t matter: According to Google, intrusive interstitials are a negative ranking factor. However, in reality, we see them on top ranking pages still.
Level of impact: Low to moderate
How to check
- Read the article ‘What Counts As an Intrusive Interstitial’ by Aleh Barysevich, published on Search Engine Journal
- Load the referring page in any web browser (eg, Safari, Chrome, Edge)
- Disable your browser’s ad blocker
- Refresh the page:
- ✅ Pass: The referring page does not have intrusive interstitials (especially on mobile viewport)
- ⚠️ Fail: The referring page has intrusive interstitials (especially on mobile viewport)
The anchor text and placement of the hyperlink appears natural and consistent with the rest of the website’s editorial guidelines
Level of importance: Preferred
Why this doesn’t: There is no evidence Google can tell if a link has been placed ‘naturally’ or otherwise – especially when the link to your target URL is published at the same time as the page itself (ie, not a niche edit). However, ensuring the link placement looks natural may reduce jealous competitors reporting it.
Level of impact: Low to moderate
How to check
Read a few recent articles on the referring domain and pay attention to how it uses outbound hyperlinks.
- ✅ Pass: The referring page links to the target URL in a natural manner consistent with its editorial standards
- ⚠️ Fail: The referring page links to the target URL in an unnatural manner
The page the hyperlink is placed on has less than 15 other hyperlinks to external sites
Level of importance: Nice to have
Why this doesn’t matter: In theory, more outbound links on a page = less link equity for your target URL. Similarly, a person is less likely to click on your hyperlink when there are many competing links on the page. But wouldn’t you want a backlink from a high-traffic page, on a well-known referring domain, even if it has hundreds of outbound links?
Level of impact: Low
How to check
Load the referring page and manually count the number of outbound hyperlinks.
- ✅ Pass: The referring page has <15 outbound hyperlinks
- ⚠️ Fail: The referring page has >15 outbound hyperlinks
Additional notes
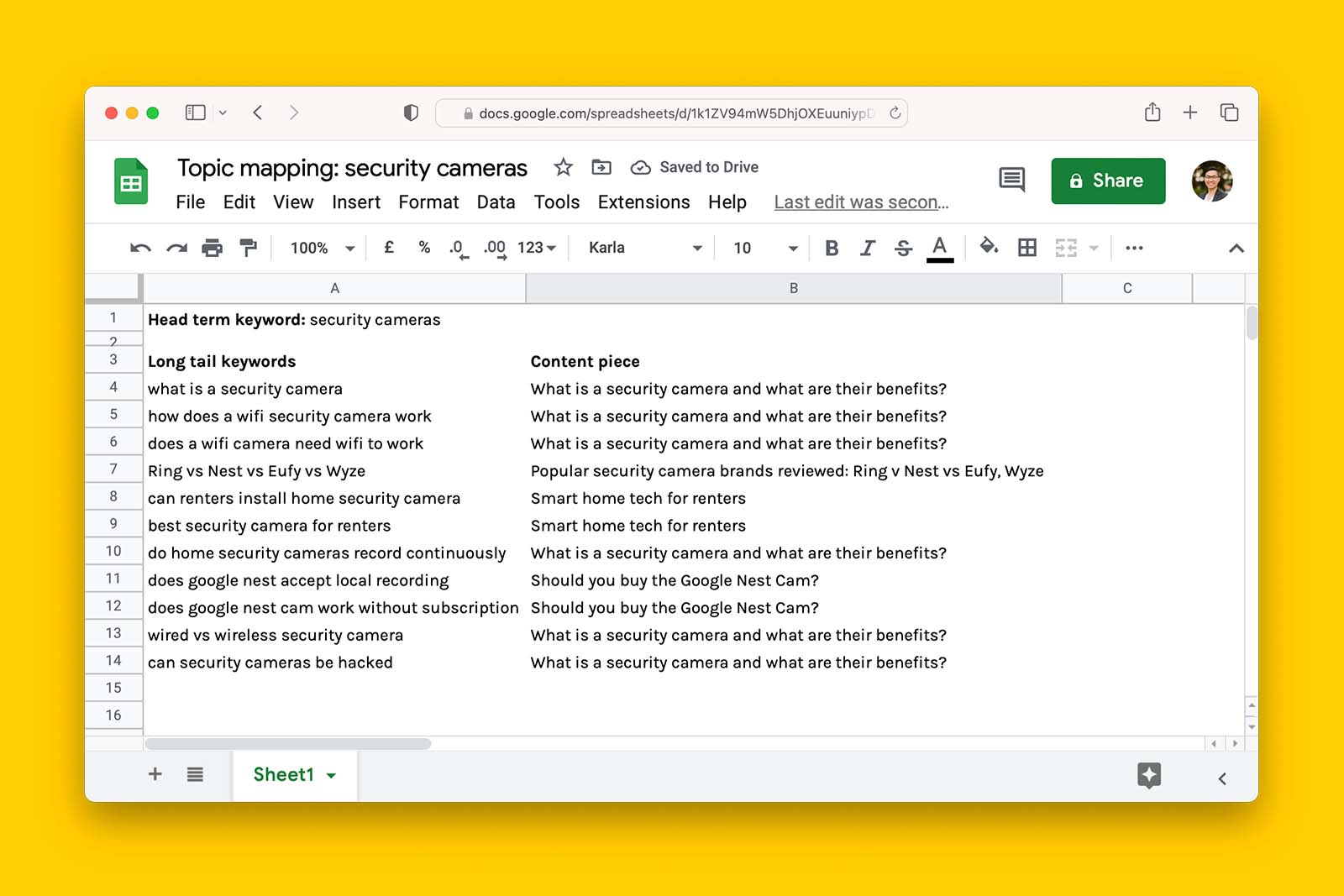
Download my 22 point backlink quality checklist
Check the quality of any backlink, save time and repeat this process by downloading my 22-point checklist, available as a Google Sheet.
Get ‘Backlink Quality Analysis Flowchart’ in high resolution
Like the flowchart?

Follow this link to access the Miro board where you may zoom in without any quality loss (no account with Miro is required).
Closing remarks
There is no such thing as a toxic backlink – only backlinks that provide value and those that do not.
Whether you’re getting a mention via digital PR, inserting a link into an existing URL, or paying for a nofollow link on Wikipedia, remember this:
There’s a backlink for every purpose.
The trick is knowing what type of backlink you need to achieve said purpose.