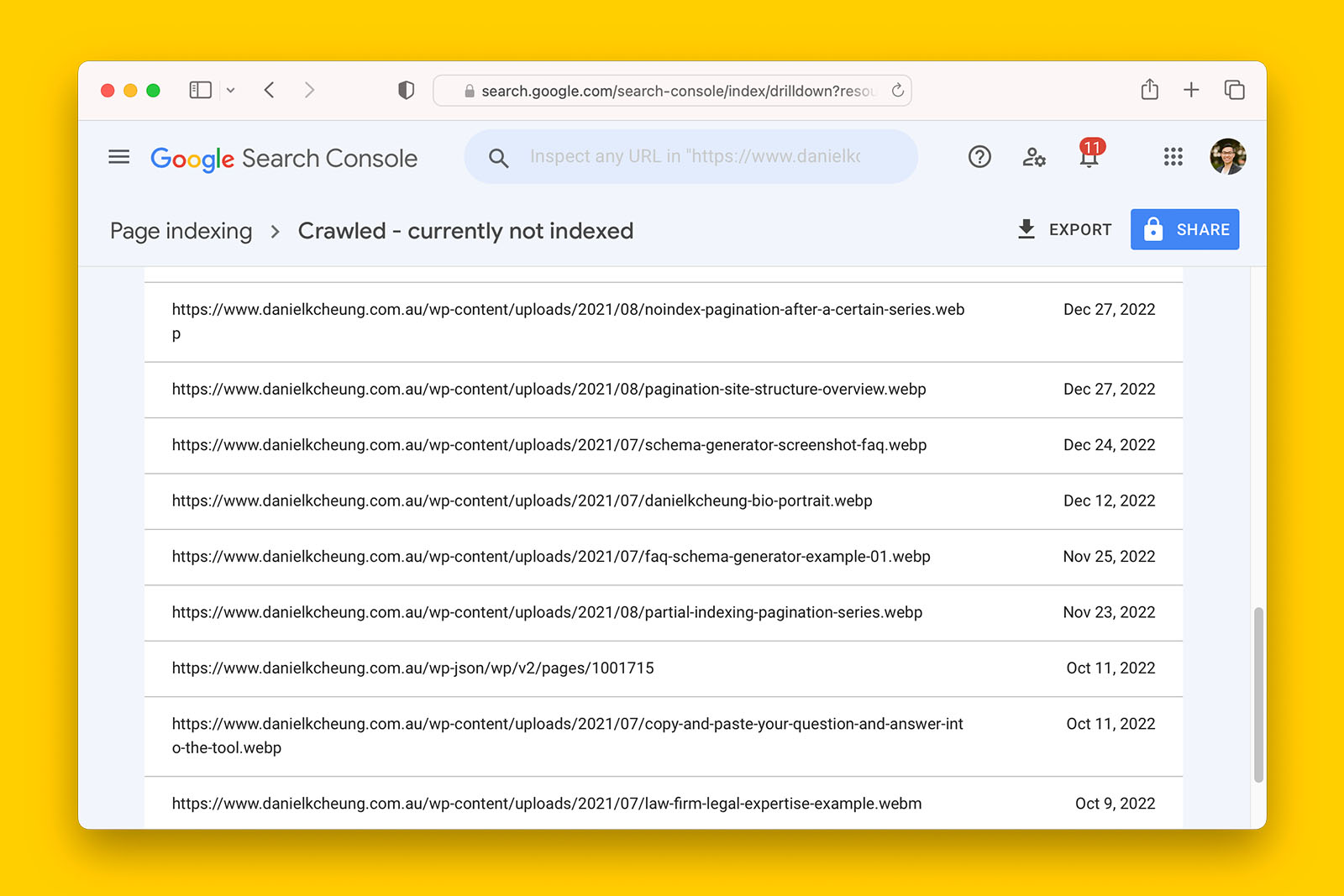
How to diagnose and fix ‘Crawled – currently not indexed’ pages
‘Crawled – currently not indexed’ is a message you will find in Google Search Console in the Page indexing report.
In this article, you’ll learn how to resolve this message so that your unique and helpful content can be found by people using Google Search.
Let’s get started.
What does ‘Crawled – currently not indexed’ mean?
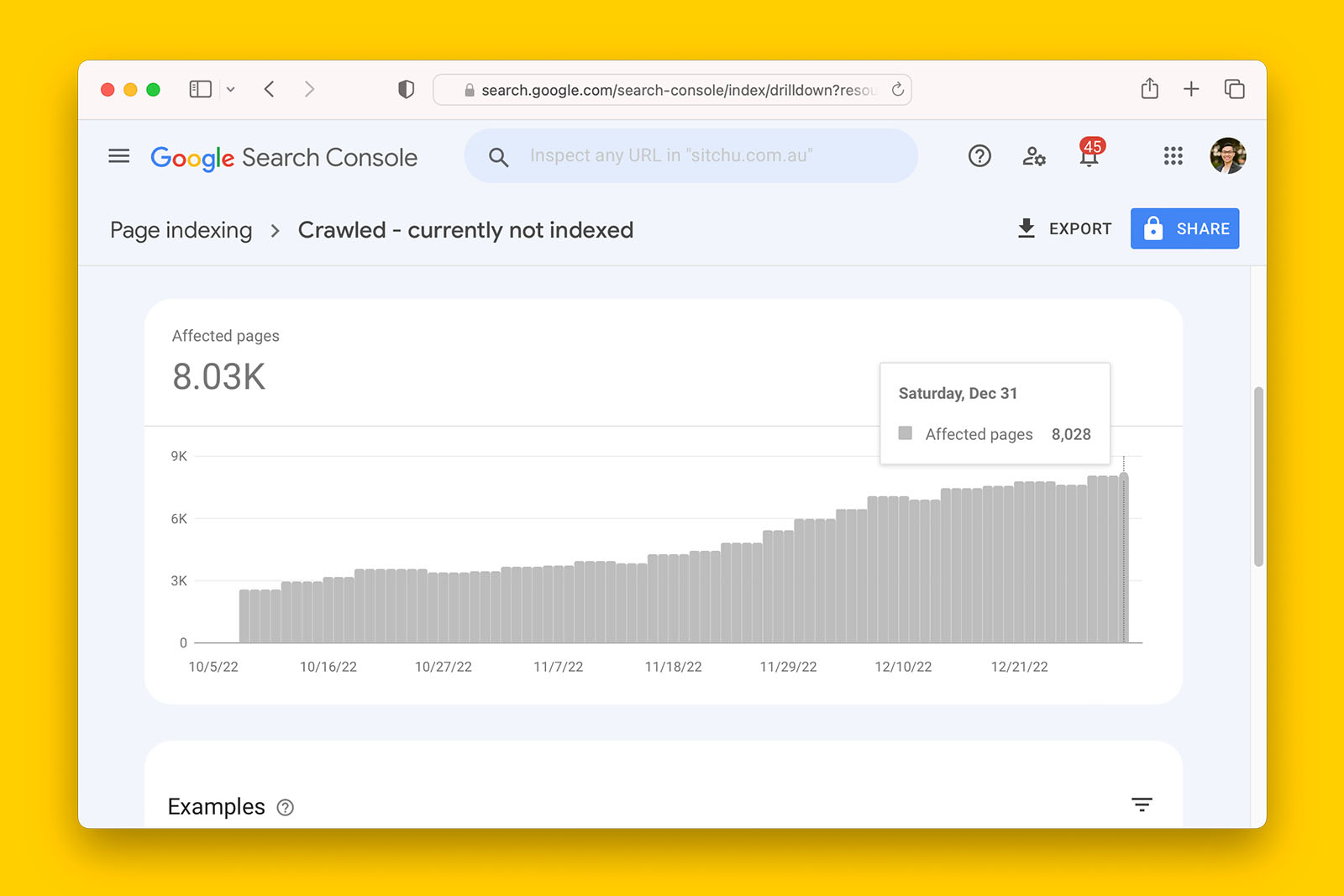
The term ‘Crawled – currently not indexed’ indicates a specific situation where a webpage has been visited (crawled) by Google’s bots, but it has not been added to Google’s index.
This means that even though Google is aware of the page and has analyzed its content, it has decided not to display it in search results.
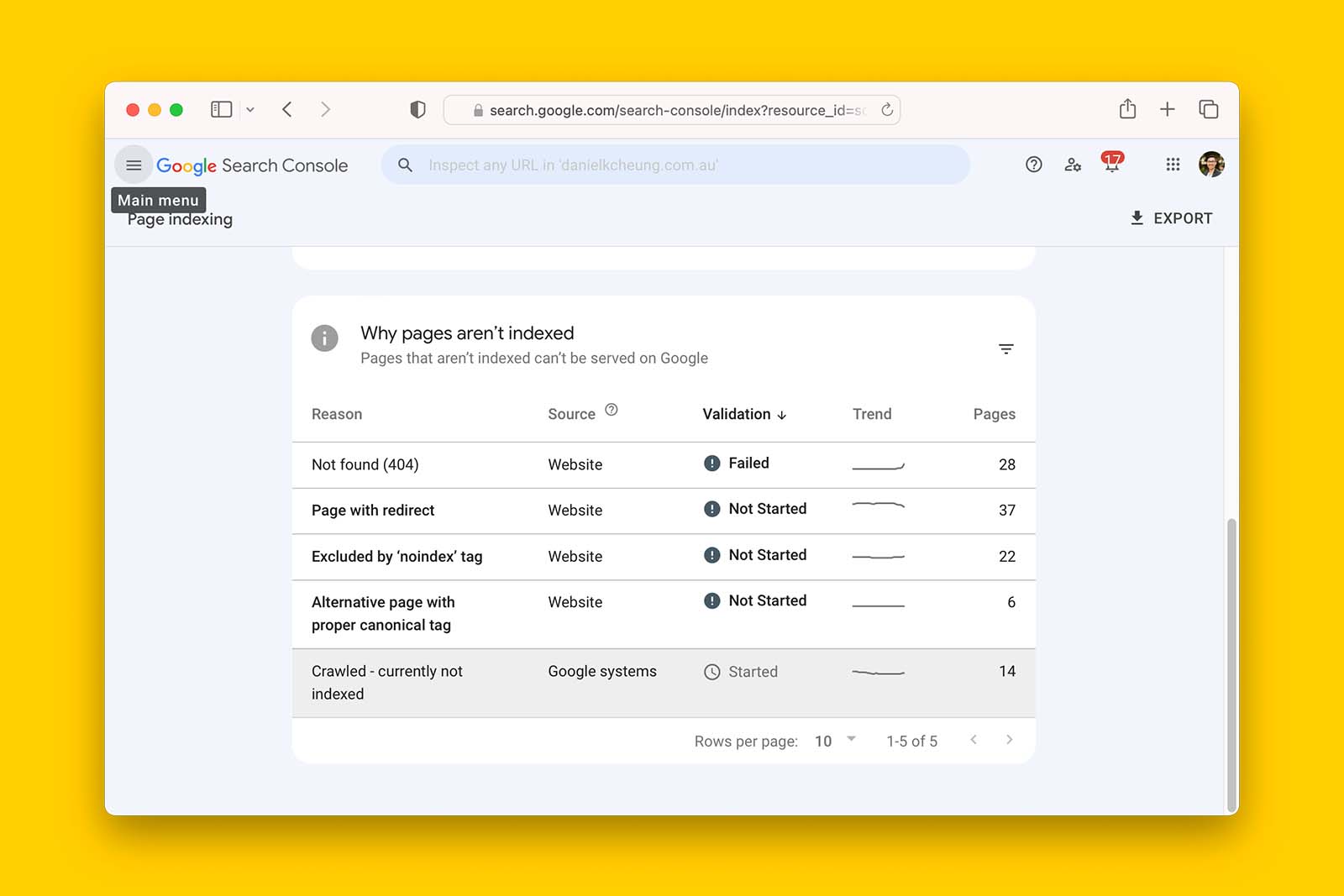
Common reasons for ‘Crawled – currently no indexed’
1. Google has difficulty rendering the content
Google wants to know what content it is committing to its index. Therefore, it needs to see what the webpage looks like and it does so with mobile-first indexing.
If the page requires extensive JavaScript or critical CSS paths have been blocked in the robots.txt file, Google cannot see the webpage and therefore cannot gauge the relevance and quality of the content.
This is one of the most common reasons why modern JS frameworks experience indexing issues.
2. Your content offers little to no new information for searchers
It costs significant resources to crawl and index the growing internet. Therefore, it is in Google’s best interest to index content that offers a different perspective to what already exists in its index.
3. The website has not demonstrated subject matter expertise in the topic of the page
Most websites on the internet stick to an overall topical theme. When a website starts branching into a completely new direction, Google may decide to delay indexing as the website has poor topical relevance and no authority on the subject matter.
4. The webpage is an orphaned URL
Google may have discovered a URL from a XML sitemap but may choose not to index the page because no other webpages have linked to it.
5. Status of the host server has changed
In rarer cases, a website may have blocked all traffic as a response to a DDoS attack. After some time, Google will begin removing pages from its index as it can longer verify the content’s existence. And when crawlers can access the website again, it may take some time for these pages to get indexed again.
6. GSC reporting issue
The data from the URL Inspection tool refreshes much quicker than that of the Index Coverage report. What this means is that if the URL Inspection tool says a page is indexed but the same URL is reported as being ‘crawled – currently not indexed’, ignore the latter information.
7. Google is experiencing indexing issues
Google has experienced indexing issues in the past where there are substantial delays in new content displaying in Google Search and Google News.
How to fix ‘Crawled – currently not indexed’ in 8 steps
The solution to this problem will depend on why you think Google has decided against adding the page to its index.
In my experience, you will probably have to address a few of these things all at once.
1. Make it easy for Google to render the content
If your analysis reveals that Google has difficulty rendering the content, this is your biggest priority.
You’ll need to get an understanding of what has happened to the website and see how this information aligns with when URLs started not getting indexed. Usually, a change to the front-end or back-end CMS is causing rendering bottlenecks.
For example, if the website got a new design and the new design requires JavaScript to render on-page content, and there were no issues with new content being indexed before the re-design, this is probably something you want to verify.
Or perhaps the website moved from one platform to another (e.g., from WordPress to headless).
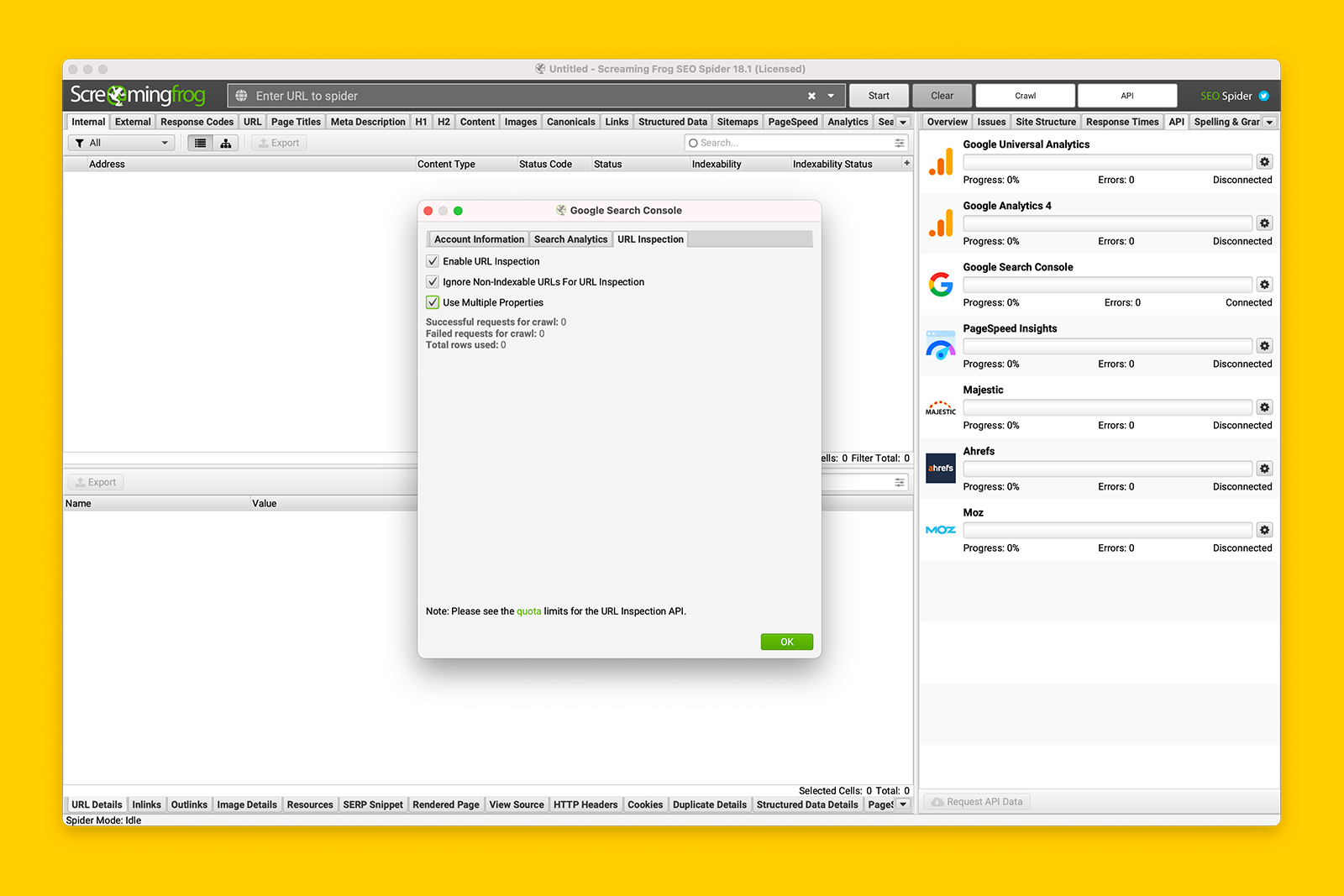
You can do this by checking if Google can render the content using the GSC URL Inspection tool.
To do this:
- In the Page indexing report, click on the magnifying icon on one of the affected pages. This will open up the URL Inspection Tool.
- Click TEST LIVE URL and wait for Google to crawl and attempt to render the page’s contents.
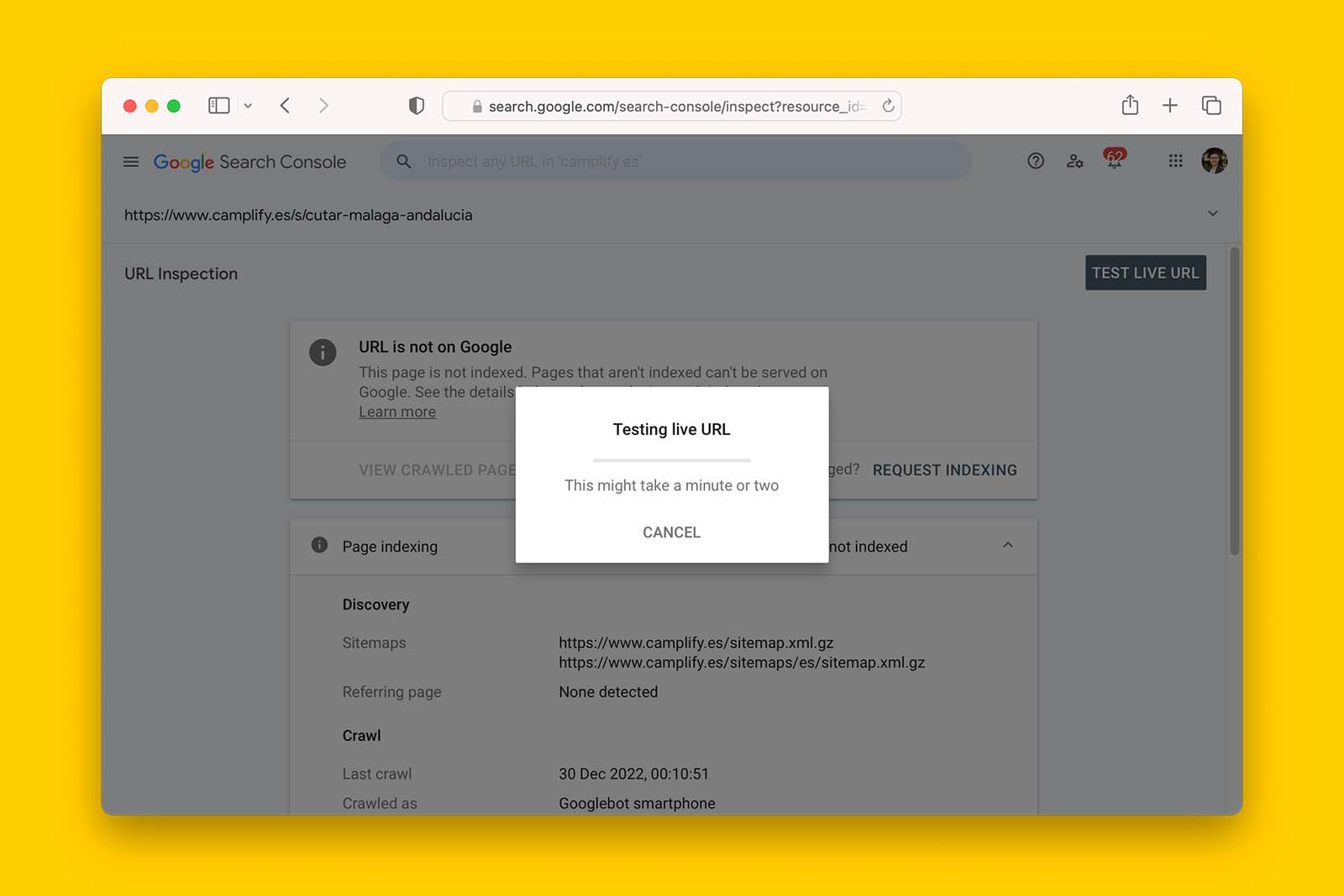
- Once the page reloads, click VIEW TESTED PAGE > SCREENSHOT and see if Google has rendered the page properly.
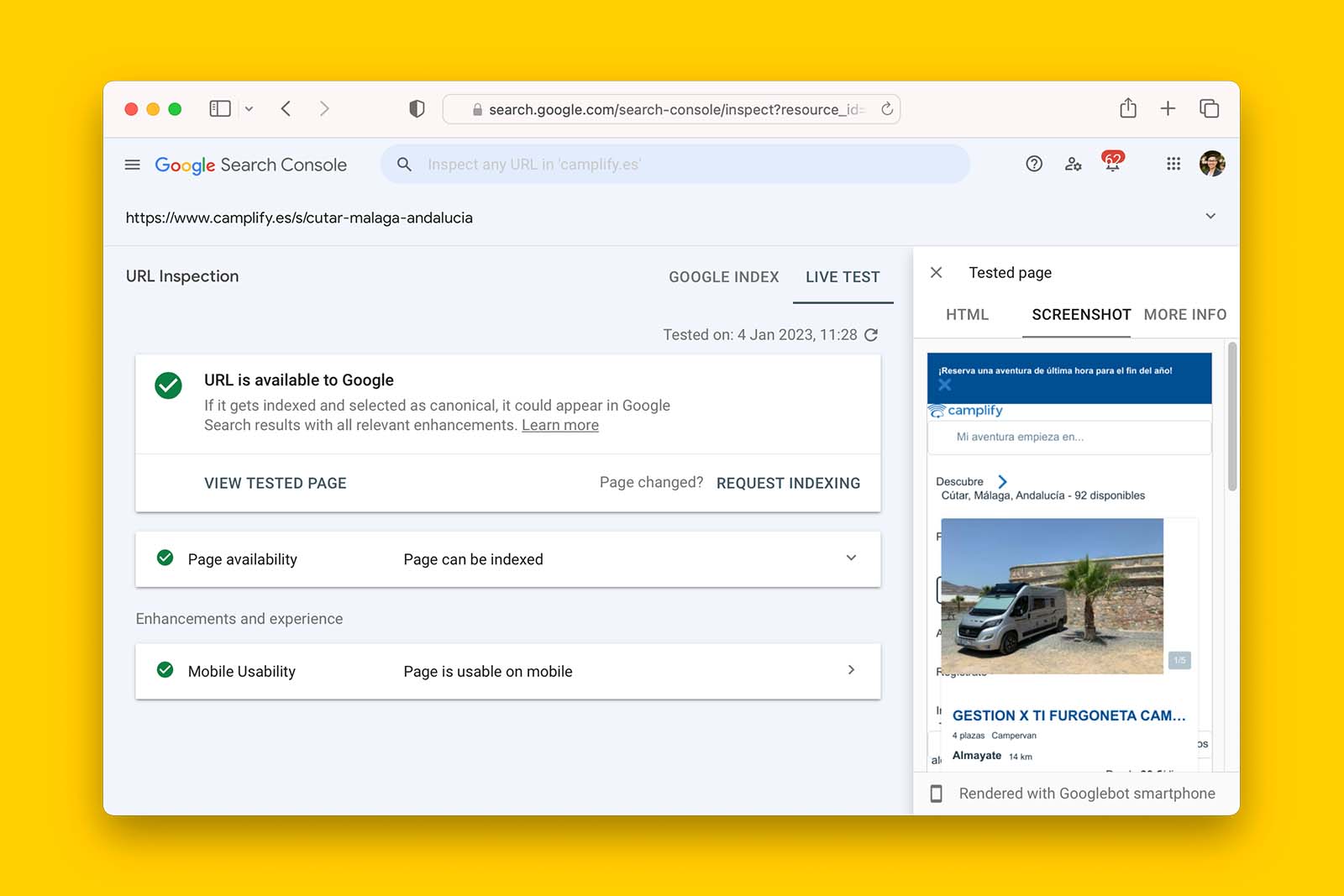
To get this information at scale, use a web crawler such as Screaming Frog SEO Spider. And for websites relying on browser rendering, follow the instructions detailed in ‘How to crawl a JavaScript (or React) website with Screaming Frog’.
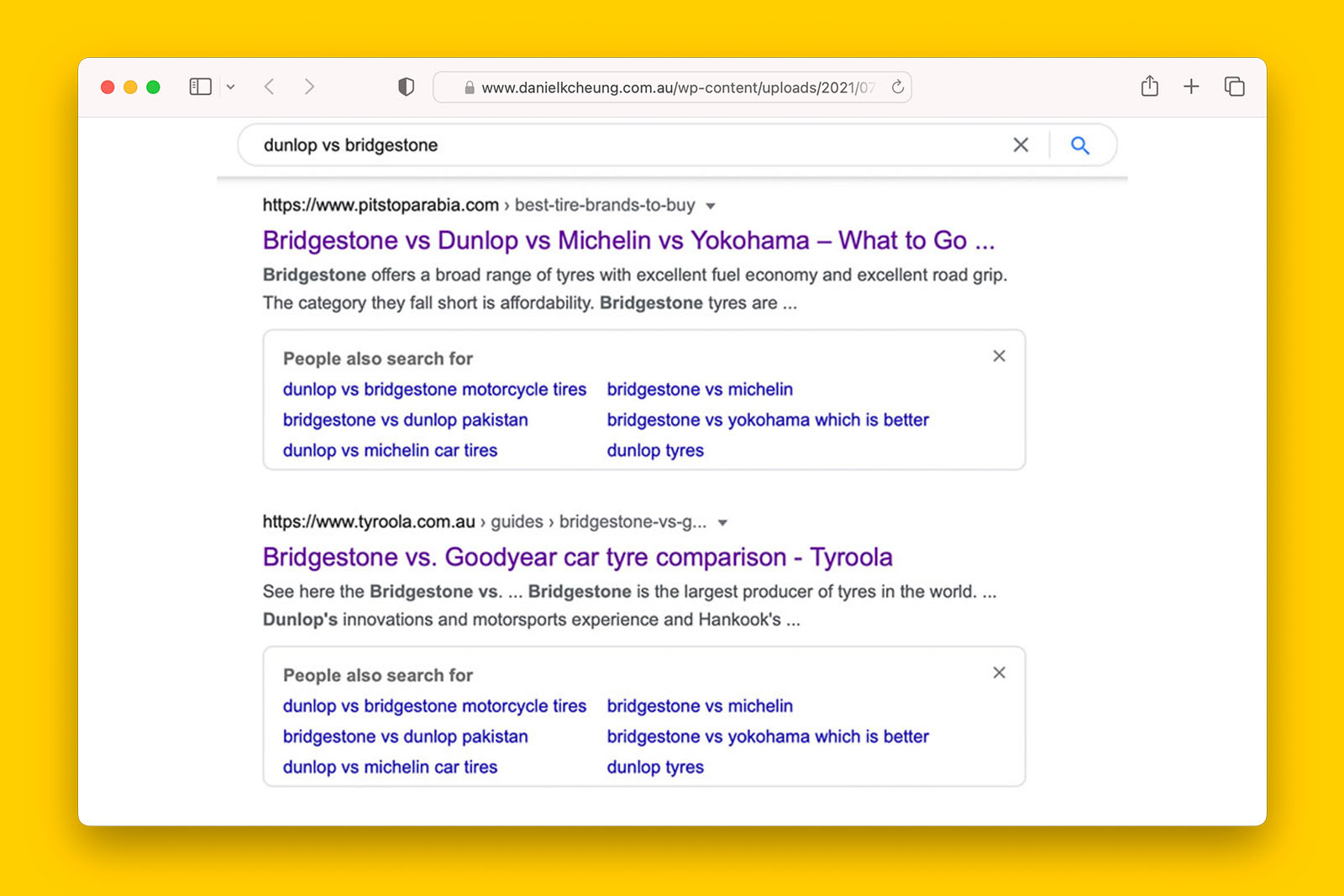
2. Offer new or different information to Google users
One of the biggest mistakes content writers and SEOs make is publishing regurgitated information.
There is absolutely no incentive for Google to index webpages with similar content to what already it has crawled, rendered and indexed.
To make matters worse, popular SEO writing tools such as Surfer SEO, Clearscope, Fraze, and copy.ai can easily encourage writers to repeat the same content that already ranks.
This is why having a structured content brief template matters.
Therefore, if one or more webpages are stuck in ‘Crawled – currently not indexed’ status for a prolonged period, you can fix this by improving the quality of the content so that the user experience is different to an already saturated SERP.
This can be done by:
- providing new information that other websites have failed to cover
- being more detailed so that the reader doesn’t have to perform additional searches
- offering a controversial opinion backed up by real experience
- addressing a particular group of people rather than a broad audience.
This means publishing a minimum number of webpages to cover the topic.
Depending on the topic, you may need 3-20 pieces of supporting content, each varying in word count and linking to each other using contextual and meaningful anchor text.
For example:
- A brick-and-mortar bridal store will need at least 3 pieces of supporting content covering different questions a customer may have in their buyer’s journey, for example:
- What are wedding dress silhouettes, how do they differ, and which one is best for me?
- Do wedding dresses need alterations? If so, which ones are most common?
- What materials are wedding dresses made from?
- An affiliate aggregator will need at least 7 educational articles covering various aspects of credit cards if they wish to rank for corresponding commercial intent queries, for example:
- Types of credit cards
- Credit card fees explained
- How to compare and pick the best credit card
- What is the difference between a credit card and a debit card?
- Guide to credit card: interest-free days, minimum repayment vs statement balance, interest rate etc
- How to read your credit card statement
- [product A vs product B]
- An eCommerce business will need at least 3 articles on each product category, for example:
- What is a video doorbell?
- [product A vs product B]
- What are the benefits of a video doorbell?
As more supporting content is published, you should see the target webpage move from ‘Crawled – currently not indexed’ to ‘Indexed’.I also recommend specifying an author and/or reviewer in each of these articles using structured data markup.
4. Link to the affected webpage from other relevant pages on the website
Adding internal links is one of the easiest things you can do in SEO.
To do this:
- Open up Google search in a browser
- In the address field, use site: search operator and add the domain
- Add a space then input a keyword
site:nerdwallet.com credit cards- Look for pages that you think can reference the URL stuck in ‘Crawled – currently not indexed’
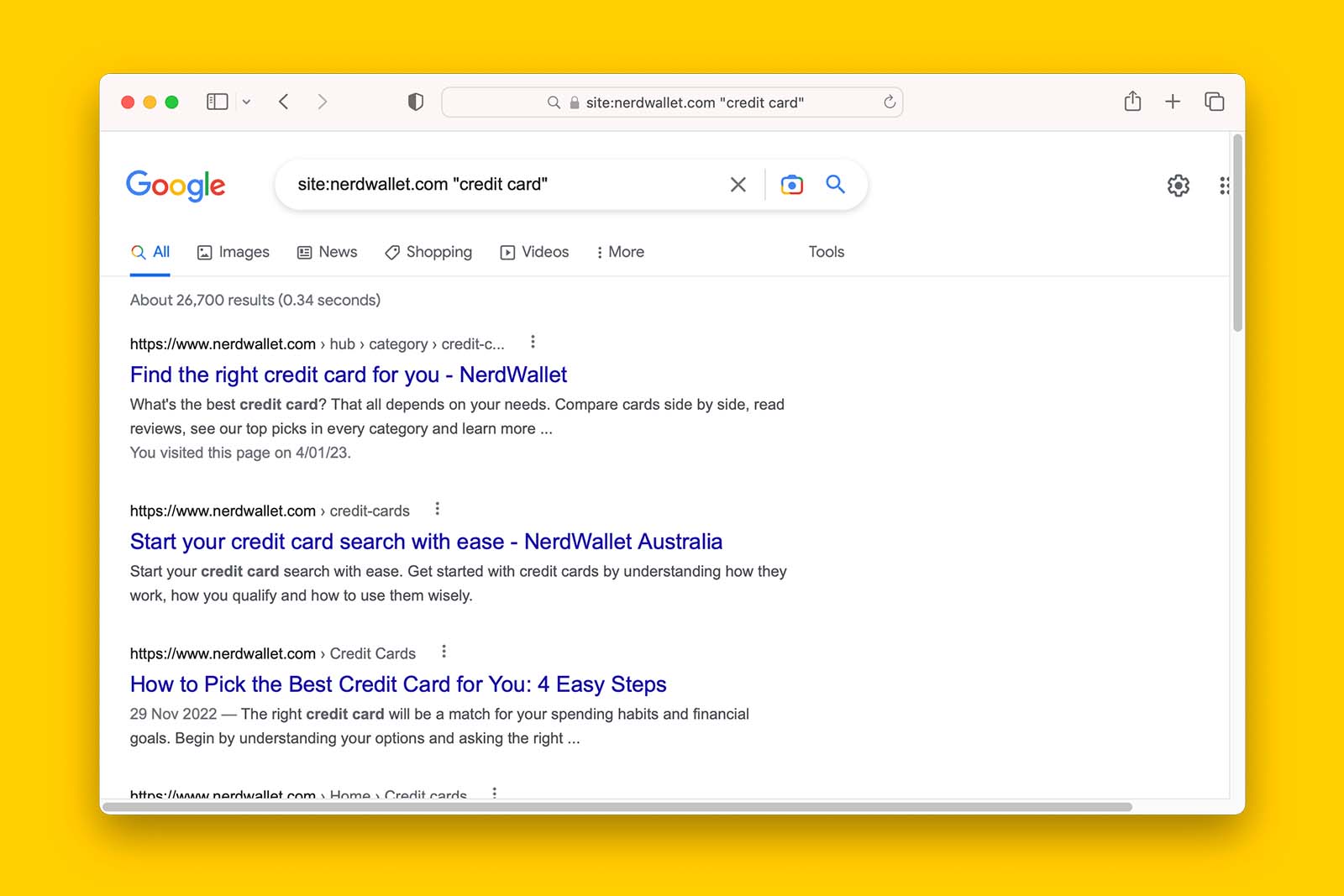
- Add an internal link to the target page from these URLs.
5. Check for bot detection and protection protocols and advise accordingly
I worked on a website that was the target of a DDoS attack. In response, all non-Australian IP addresses were blocked. Within 72 hours, Google began de-indexing webpages, including the homepage as it could no longer access the website.
After much explaining and negotiating, I was able to convince decision-makers to remove the geofencing and most URLs were re-indexed.
However, it took a week and a mixture of non-indexed URLs was being reported as ‘Crawled, currently not indexed’, ‘Discovered – currently not indexed’, or ‘Blocked due to access forbidden (403)’.
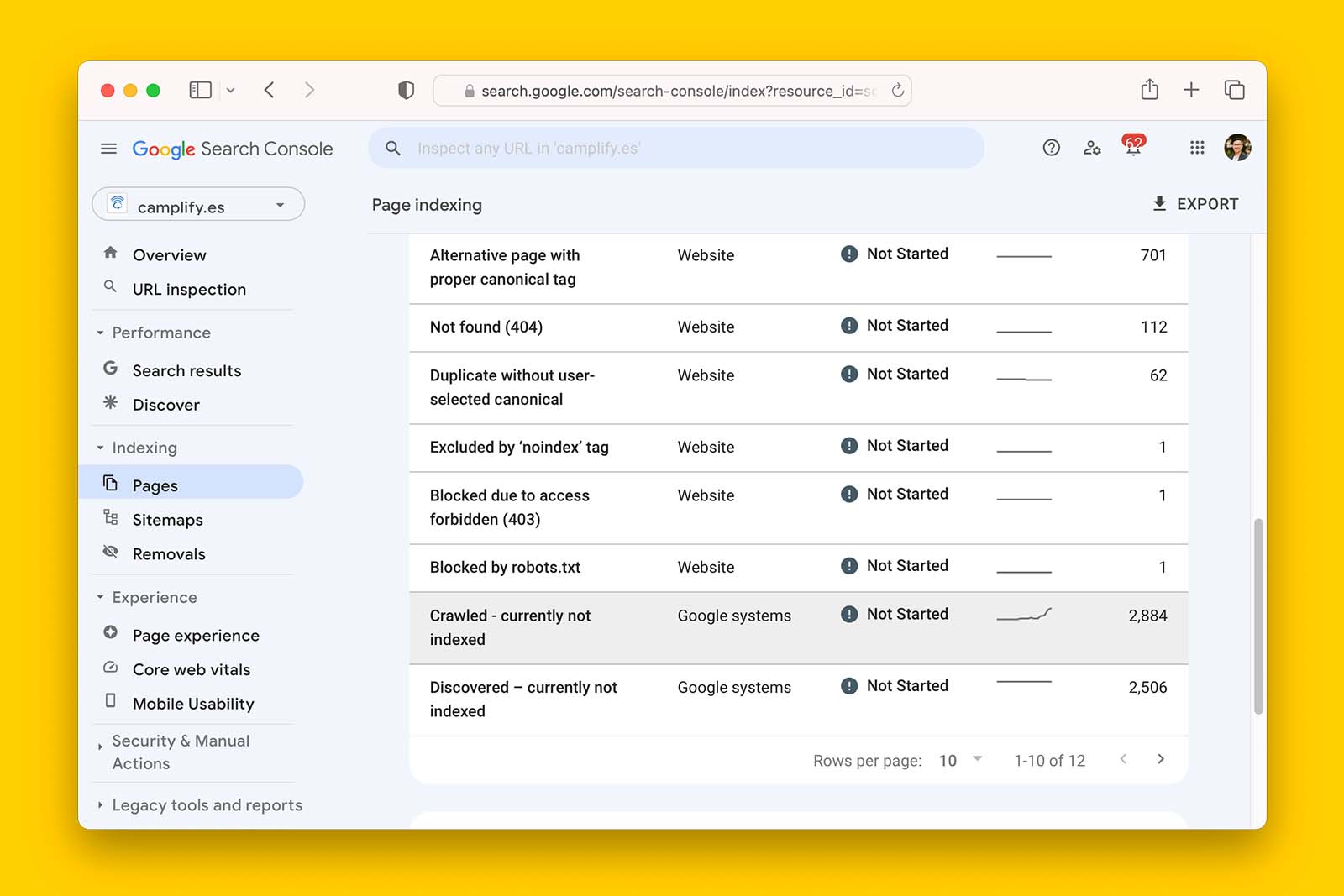
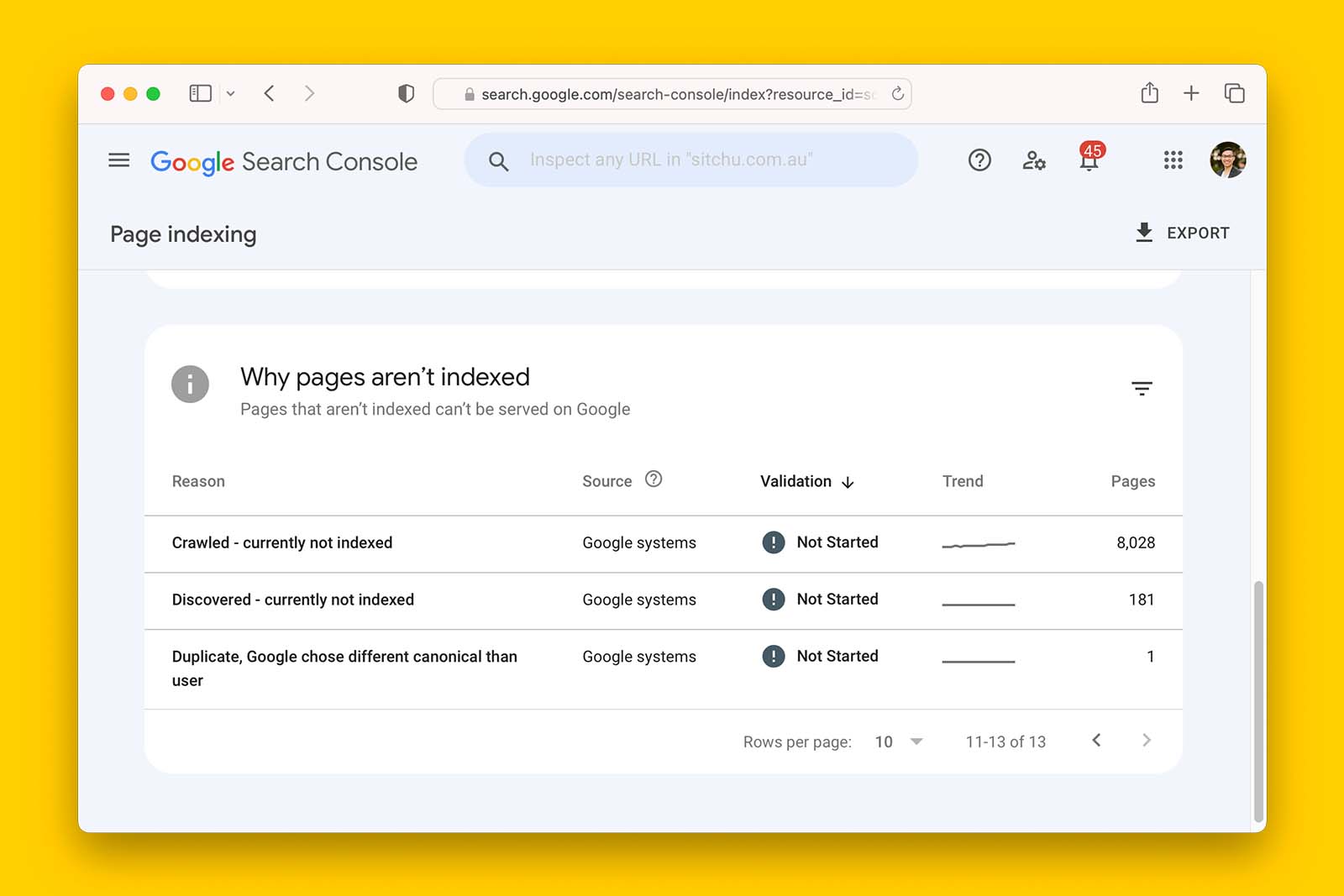
6. Compare URL Inspection Tool results against Page indexing report
Data in Search Console’s Page indexing report is refreshed at a slower cadence than URL Inspection Tool. Therefore, some pages reported as ‘Crawled – currently no indexed’ may have already been indexed.
For example, in the following screenshot, the last update to the Page indexing report in Google Search Console is at least 72 hours behind.
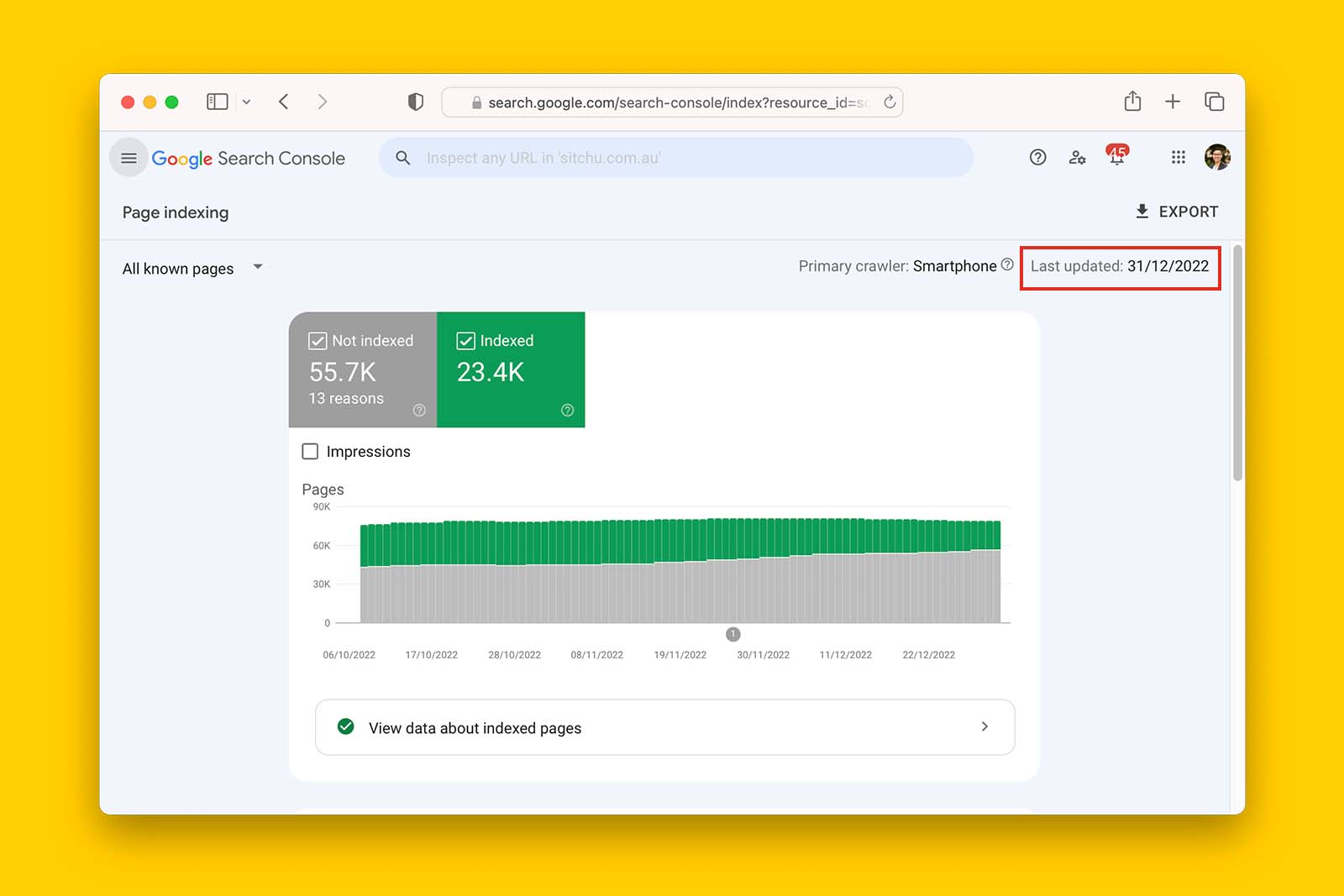
To verify if this is the case:
- manually inspect each URL in GSC if you have a small number of affected pages
- if you have a large number of pages to check, connect Screaming Frog SEO Spider to Google Search Console URL Inspection API and run a crawl.
7. Check Google Search status dashboard
Back on July 15, 2022, Google confirmed it was having issues indexing new content (source).
In response to this, it launched a Google Search status dashboard.
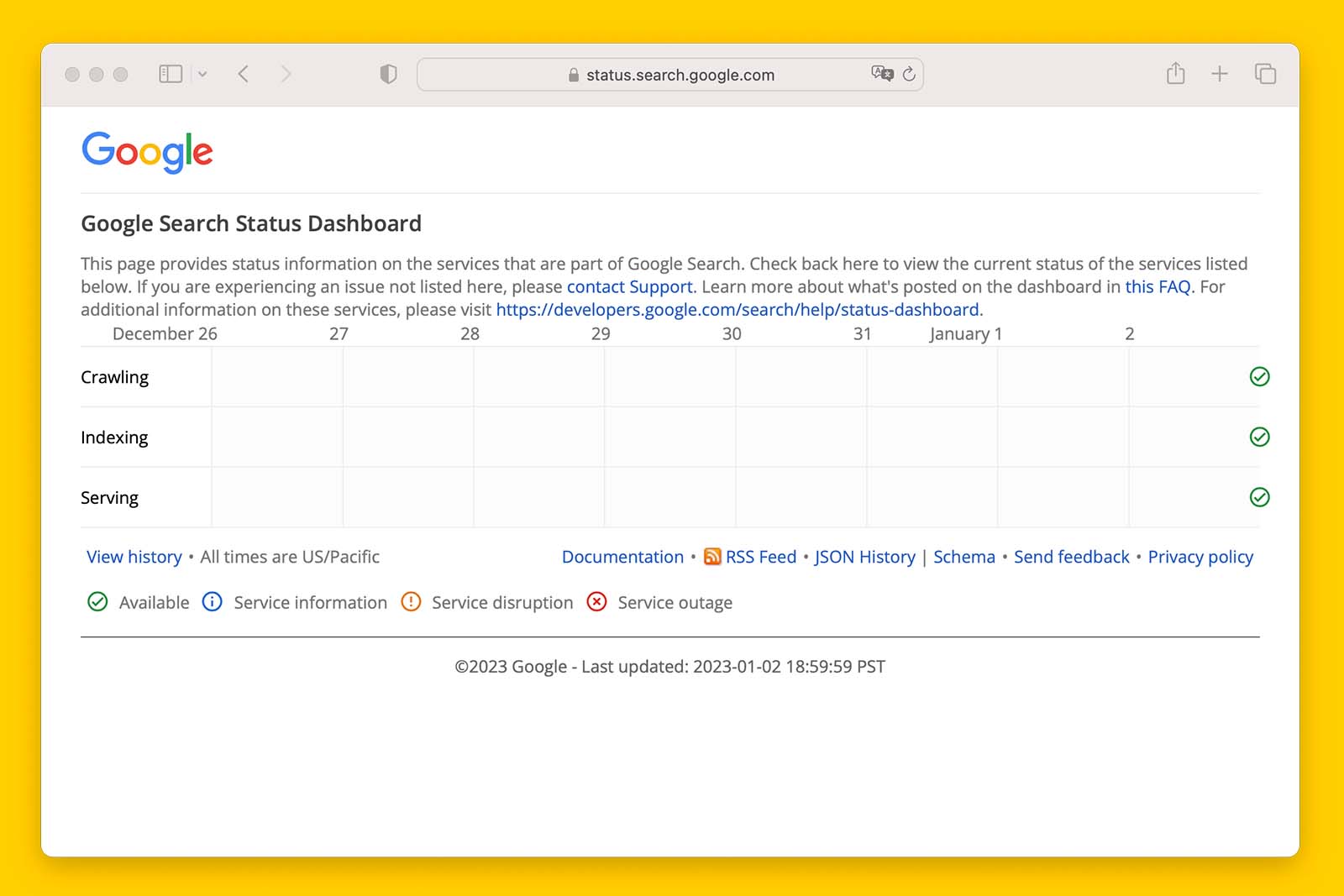
If you truly believe the website has no technical issues and the content on the page is unique to what already exists on the SERPs, and the Google Search status dashboard reports that Google is experiencing indexing issues, then there is nothing you can do but wait for Google to resolve things on their end.
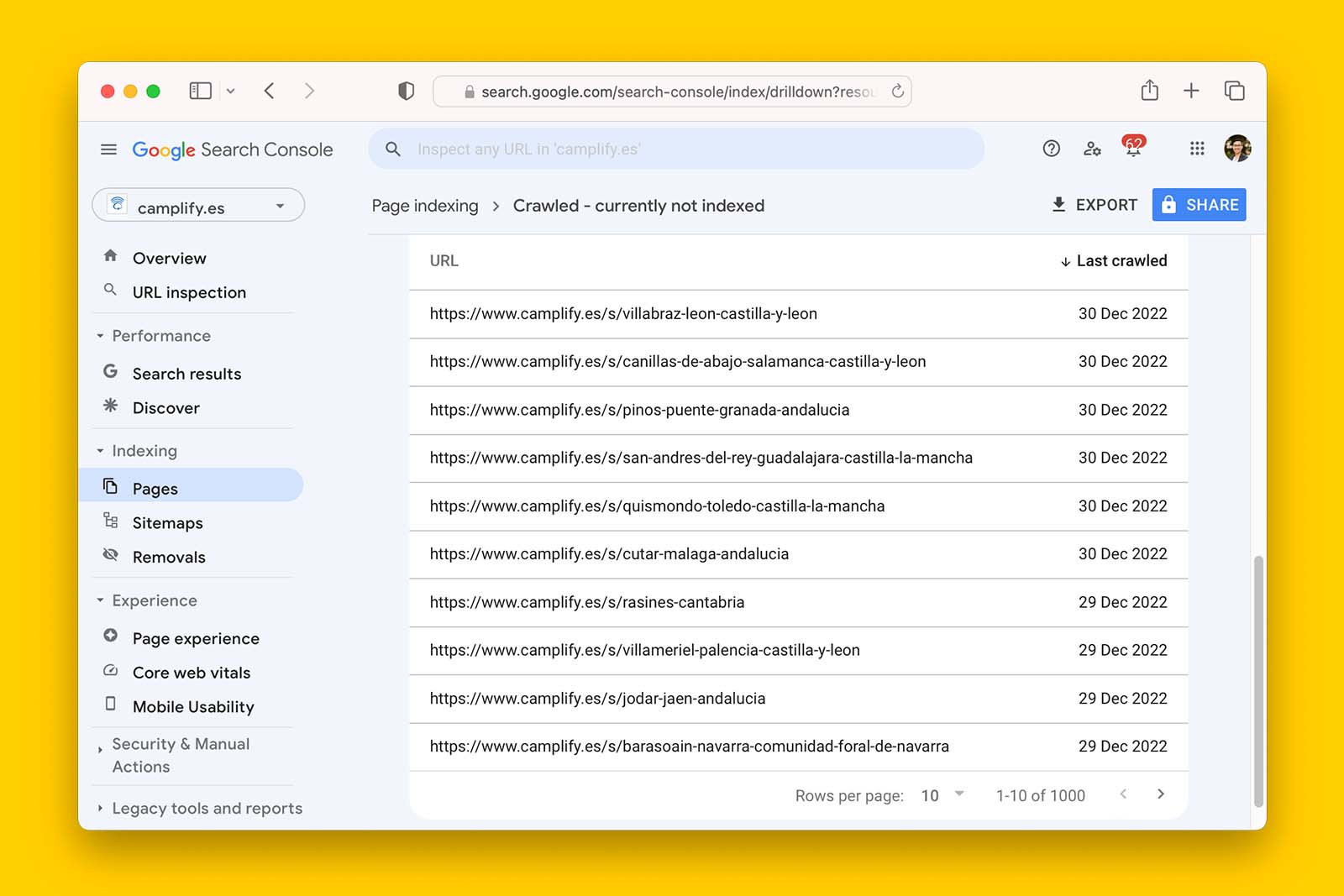
8. Identify a common pattern among affected URLs to form a hypothesis to test
SEO is a continual process of making hypotheses, testing, observing, and making hypotheses again. Your job is to gather the data and make sense of it.
Google tends to leave clues as to why it is not indexing a page. The fact that it has crawled a webpage and decided against indexing is a big hint.
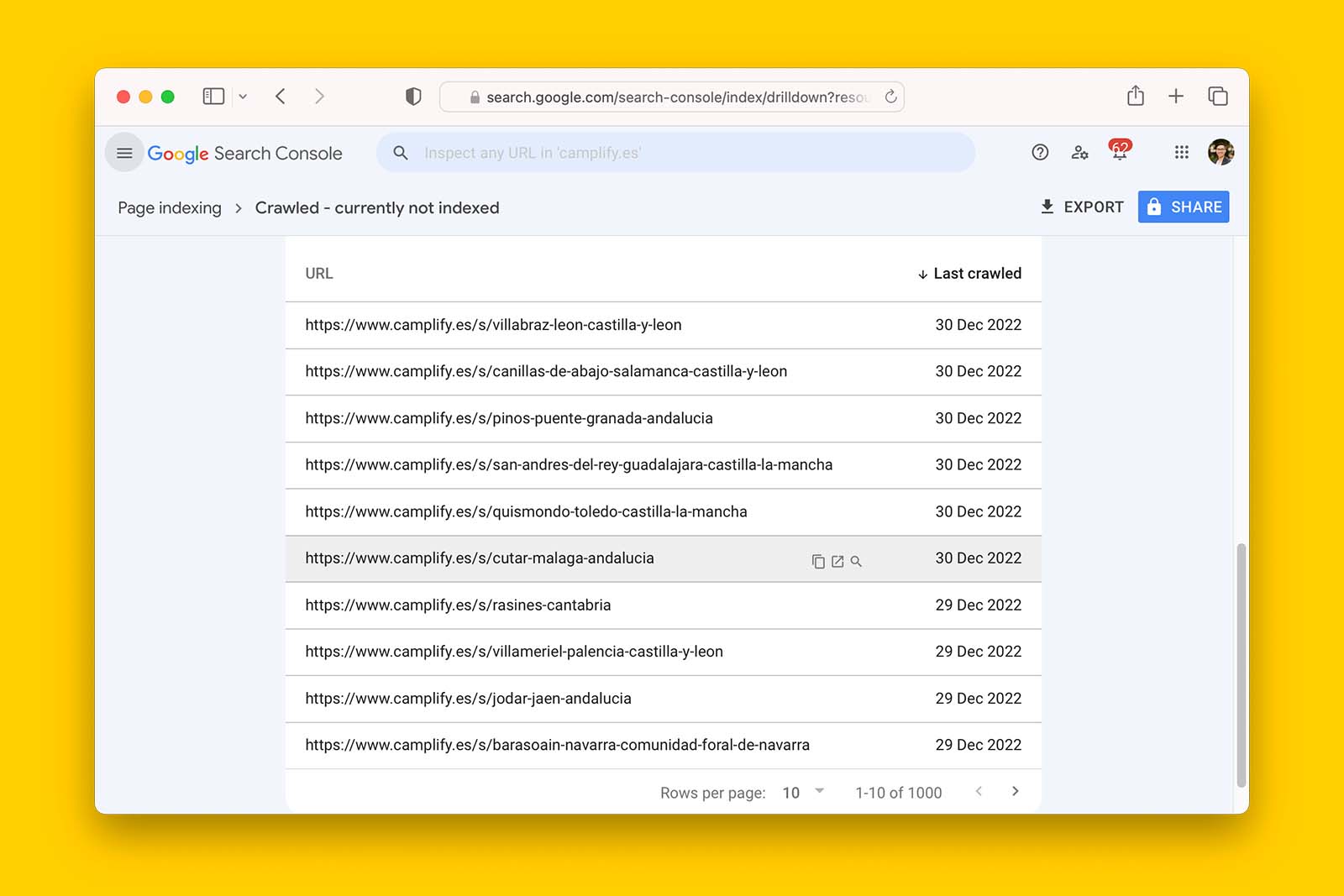
Once you have extracted a complete list of all ‘Crawled – currently not indexed’ URLs, look for page templates or page elements that are common in the affected URLs.
And since you know Google has successfully crawled these URLs, you can use the insights the crawl stats report in GSC provides to support your hypotheses.
For example, you can assume that URLs that have been crawled but not indexed fit into Googlebot’s discovery function. In GSC, you can extract a list of these URLs that Google has discovered in the last 90 days.
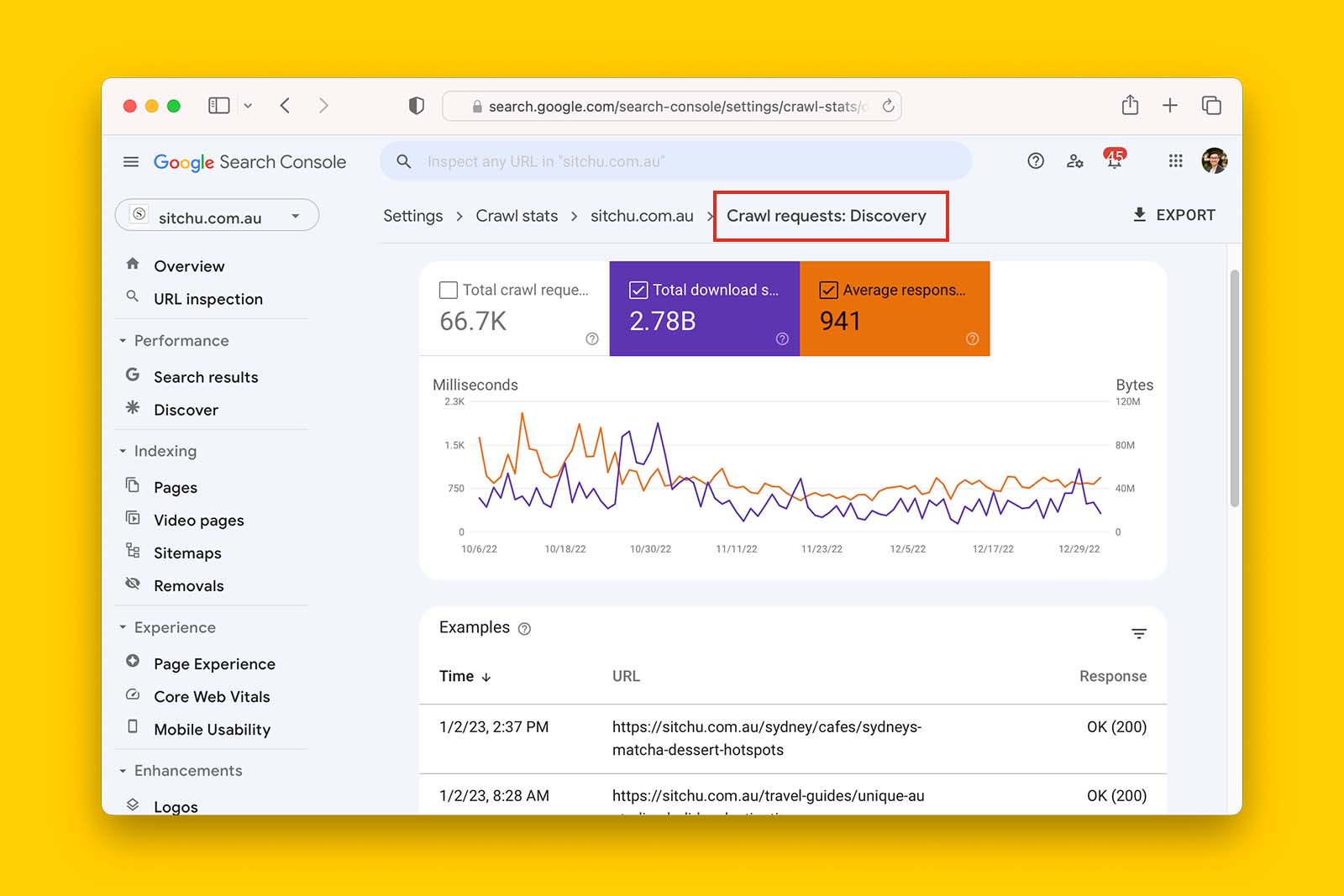
Then you can use Screaming Frog SEO Spider in List Mode, connect the crawl to Google PageSpeed Insight API, grab Core Web Vital data, and see if there is a correlation between non-indexed URLs and poor CWV metrics. And since you’ve crawled these URLs, you can explore if there are any inconsistencies in their content quality, page titles, headings, meta descriptions, inbound links, html vs rendered html, or canonical tags.Alternatively, you can extract a list of CSS or JavaScript from GSC crawl stats to see if they’re being blocked in robots.txt.
FAQs
In closing
When significant resources have been used to publish useful content, having that content not discoverable on Google Search is extremely frustrating and costly.
In most cases, there is something in the front end or content that is causing Google to say, “Thanks but no thank you”.
Your role as an SEO is to figure out if an indexing problem exists and if so, does it exist on Google’s end or your end. Then it is a matter of identifying what are the most likely factors contributing to the issue(s), t-shirt sizing them in terms of effort and impact, and prioritising them.